【 研究背景 】
近年來受全球氣候變遷的影響,氣候變異劇烈且頻繁,臺灣極端降雨發生頻率有逐漸升高之趨勢,將影響既有水庫滯洪能力,而提高下游集水區遭受洪水風險。依「水利建造物檢查及安全評估辦法」規定,重要水庫需定期辦理整體安全檢查與評估。水庫安全評估工作項目眾多,針對水庫集水區水文相關分析工作,應包含年最大雨量分析、洪峰流量分析、河道/潰壩洪水演算,以及設計洪水評析等。而現行針對設計洪水評析項目中的「可能最大降水量」與「可能最大洪水量」,目前尚未有明確的計算方式可供參考,因此迫切需要提出解決方案。
【 研究目的 】
台灣四面環海,不僅漁業發達,亦位居海上重要航道,往來船舶數量眾多,目前有安裝船舶自動識別系統(Automatic Identification System, AIS)的多為大噸位船舶,小型漁船多數並未安裝,因此造成大小船舶碰撞事件不斷。交通部已於107年7月27日修正「船舶設備規則」第242條之3,公告要求總噸位二十以上的各式船舶均須裝設AIS。
我國漁船出海作業人員申報主要以書面申報為主,船隻於出海前需至安檢所遞交相關申請文件,而安檢所需派員登檢出海人員之身分,但因漁民出海作業擔心身分證明文件遺失或污損,常以拷貝文件替代或是以出海作業時間緊迫,要求安檢人員縮短檢驗時間,導致出海人員身分驗證難以確實落實。
【 執行成果 】
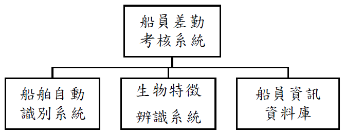
●為了人員安全與有效防止冒名出港,並簡化查驗作業程序,本研究規劃建立船員差勤考核系統。本系統包含AIS設備與生物特徵辨識系統,並介接船員資訊資料庫,系統架構如圖1所示。
【 Research Background 】
Affected by global climate change in recent years, climate variability is severe and frequent, and the frequency of extreme rainfall in Taiwan is gradually increasing, which will affect the flood detention capacity of existing reservoirs and increase the risk of flooding in downstream catchment areas. According to the "Water Conservancy Construction Inspection and Safety Assessment Measures", important reservoirs need to undergo regular overall safety inspections and assessments. There are many items in the reservoir safety assessment work. For the hydrological analysis of the reservoir catchment area, it should include the annual maximum rainfall analysis, flood peak flow analysis, river channel/dam break flood calculation, and design flood analysis. However, there is currently no clear calculation method for the "possible maximum precipitation" and "possible maximum flood" in the design flood evaluation and analysis project, so there is an urgent need to propose a solution.
【 Research purposes 】
Surrounded by the sea, Taiwan not only has a well-developed fishery industry, but also is located in an important sea lane. There are a large number of ships passing by. At present, most of the ships with automatic identification system (AIS) installed are large-tonnage ships, and most of the small fishing boats are not installed. Collision incidents of large and small ships continue. The Ministry of Communications has amended Article 242-3 of the "Ship Equipment Regulations" on July 27, 2017. The announcement requires that all types of ships with a gross tonnage of 20 or more must be equipped with AIS.
The declaration of fishing boat operators in my country is mainly based on written declaration. Before going to sea, the vessel needs to submit the relevant application documents to the security checkpoint, and the security check needs to send personnel to check the identity of the personnel who go to sea. However, fishermen are worried about the loss of identity documents when they go to sea. or defaced, copy documents are often used instead, or due to the tight time of going to sea, security personnel are required to shorten the inspection time, which makes it difficult to verify the identity of personnel going to sea.
【 Implementation results 】
●In order to ensure the safety of personnel, effectively prevent false names from leaving the port, and simplify the inspection procedures, this study plans to establish a crew attendance assessment system. This system includes AIS equipment and biometric identification system, and interfaces with the crew information database. The system architecture is shown in Figure 1.
圖1 船員差勤考核系統架構圖
Structure diagram of crew duty assessment system
船舶自動識別系統(Automatic Identification System, AIS)係結合「全球定位系統(GPS)」與「無線電特高頻(VHF)」之通信技術,連續並自動發射航行訊息,有效涵蓋範圍大約20至30海浬,可提供船舶間與船岸間航行安全資訊之傳遞。
過去曾發生漁船出海作業人員拿影印文件冒名申報出港的情形,為了確認登船者為本人,必須進行身分驗證。身分驗證通常有三類方式:(1)知識類(Knowledge):使用者知道的事物,例如帳號及密碼、安全問題等。(2)持有類(Ownership):使用者才有的事物,例如憑證、晶片卡等。(3)固有類(Inherence):使用者的生物特徵,例如指紋、虹膜、臉型等。前二類驗證方式由其他人代替進行的可能性較高,而生物特徵僅本人持有,仿製的困難度較大。目前許多公家機關與公司行號都以指紋辨識作為差勤管理或是門禁控制。然而,任何的身分驗證技術都有其限制,必須經過不斷的改善與時俱進。
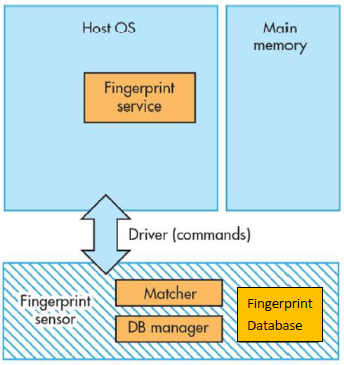
現時的指紋驗證技術有兩種:主晶片上比對(Match-on-Host)及感測器內比對(Match-in-Sensor)。傳統的Match-on-Host認證方式安全性較低(如圖2),因為指紋資料會與處理器進行資料傳輸,而成為硬體攻擊和惡意軟體攻擊的機會。而新一代的Match-in-Sensor技術透過在特製的完整封裝系統單晶片(System on a Chip, SoC)內獨立執行,並與主作業系統完全隔離,增加安全性(如圖3)。其他提高指紋辨識安全性的方式有:增加指紋之辨識面積,面積增加,誤判率則相對降低;利用機器學習,辨別假體指紋與真人指紋之差異等。
透過指紋驗證技術進行船員身分確認,並連結船員資訊資料庫,提供給安檢所登檢確認出海人員之身分。此外,船舶自動識別系統更可提供船位等船舶相關動、靜態資訊,以利公務機關進行管理。
The Automatic Identification System (AIS) is a combination of "Global Positioning System (GPS)" and "Very High Frequency (VHF)" communication technology, which continuously and automatically transmits navigation information, effectively covering a range of about 20 to 30 nautical miles 浬, which can provide the transmission of navigation safety information between ships and between ships and shores.
In the past, there have been situations where operators of fishing boats used photocopied documents to declare their departure from the port under false names. In order to confirm that the person boarding the ship is the person, identity verification must be carried out. There are generally three types of identity verification methods: (1) Knowledge (Knowledge): things that the user knows, such as account numbers and passwords, security questions, and so on. (2) Ownership: Things only available to users, such as certificates, chip cards, etc. (3) Inherence: the biological characteristics of the user, such as fingerprints, irises, and face shapes. The first two types of verification methods are more likely to be replaced by other people, while the biometrics are only held by the person himself, and it is more difficult to imitate. At present, many public agencies and companies use fingerprint recognition as attendance management or access control. However, any authentication technology has its limitations and must be continuously improved to keep pace with the times.
Currently, there are two types of fingerprint verification technologies: Match-on-Host and Match-in-Sensor. The traditional Match-on-Host authentication method has low security (as shown in Figure 2), because the fingerprint data will be transmitted with the processor, which becomes an opportunity for hardware attacks and malware attacks. The new generation of Match-in-Sensor technology is independently implemented in a special complete package System on a Chip (SoC) and completely isolated from the main operating system to increase security (Figure 3). Other ways to improve the security of fingerprint identification include: increasing the identification area of fingerprints, increasing the area, and relatively reducing the false positive rate; using machine learning to identify the difference between fake fingerprints and real fingerprints, etc.
The identity of the crew is confirmed through fingerprint verification technology, and it is linked to the crew information database, which is provided to the security checkpoint for boarding to confirm the identity of the seafarers. In addition, the ship's automatic identification system can also provide ship-related dynamic and static information such as ship position, so as to facilitate the management of public agencies.
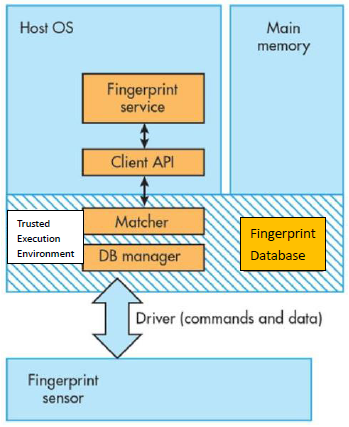
圖2 Match-on-Host
圖3 Match-in-Sensor
內含船員差勤考核系統架構、船員差勤考核裝置管理系統之設計分析、船員差勤考核系統之功能分析及測試、船員差勤考核系統功能限制及涵蓋範圍。並協助開發相關實驗設備與提供實測研究之比較分析報告,以利辦理相關推廣與規劃事宜。
It includes the structure of the crew attendance assessment system, the design analysis of the crew attendance assessment device management system, the functional analysis and testing of the crew attendance assessment system, the functional limitations and coverage of the crew attendance assessment system. And assist in the development of relevant experimental equipment and provide comparative analysis reports of actual measurement research, so as to facilitate related promotion and planning matters.